In “Exploring the Cognitive Stimulation Approach for At-Risk Individuals,” we delve into the potential benefits of cognitive stimulation for individuals at risk of decline. This article focuses on providing in-depth coverage of the specific subject, without overwhelming you with unnecessary background information. By understanding how cognitive stimulation can positively impact at-risk individuals, we hope to shed light on this approach and its potential to enhance their overall well-being, cognitive abilities, and quality of life. So sit back, relax, and let's embark on this informative journey together!
Understanding Cognitive Stimulation
Cognitive stimulation refers to the process of engaging and stimulating the brain's cognitive functions to promote and maintain brain health. It involves activities and exercises that challenge the brain, encouraging it to actively use and strengthen its cognitive abilities. By regularly engaging in cognitive stimulation, individuals can improve their memory, problem-solving skills, and overall cognitive functioning, ultimately reducing the risk of cognitive decline.
Definition and Basics of Cognitive Stimulation
Cognitive stimulation encompasses a wide range of exercises and activities that target various cognitive domains, such as memory, attention, language, and executive functions. These activities are specifically designed to challenge the brain and promote its plasticity, allowing for the creation and strengthening of neural connections. The goal of cognitive stimulation is to improve cognitive performance and delay the onset of cognitive decline.
Tools and methodologies for cognitive stimulation vary widely and can include brain-training games, puzzles, arts and crafts, music, language learning, and physical activities that involve cognitive engagement. These tools and techniques can be tailored to individual preferences and abilities, ensuring that the cognitive stimulation activities are both enjoyable and effective.
Parameters Defining At-Risk Individuals
Definition and Identification of At-Risk Individuals
At-risk individuals are those who have factors that increase their vulnerability to cognitive decline or impairment. These individuals may have certain characteristics or conditions that make them more susceptible to cognitive deficiencies. Identifying at-risk individuals is crucial in order to provide them with appropriate cognitive stimulation interventions and support.
Factors Contributing to Being At-Risk
Several factors contribute to an individual's classification as at-risk for cognitive decline. These factors can include but are not limited to age, genetics, lifestyle choices, and pre-existing medical conditions. Older adults are particularly at-risk due to the natural aging process, while individuals with a family history of cognitive decline or neurodegenerative diseases may also be more predisposed. Lifestyle choices, such as a sedentary lifestyle, poor nutrition, and lack of mental stimulation, can further increase the risk of cognitive decline.
Common Cognitive Deficiencies in At-Risk Individuals
Pattern Recognition Issues
At-risk individuals often struggle with pattern recognition, which refers to the ability to identify, analyze, and understand patterns in information. This cognitive ability plays a crucial role in memory, problem-solving, and abstract thinking. Any impairment or deficiency in pattern recognition can pose significant challenges in daily functioning and overall cognitive performance for at-risk individuals.
Memory-Related Problems
Memory-related problems are prevalent in at-risk individuals, particularly as they age. These individuals may experience difficulties with short-term memory, such as remembering recent events or information. Long-term memory can also be affected, leading to a decreased ability to recall past memories, names, or important details. Memory deficiencies can have a profound impact on an individual's daily life and can significantly hinder their independence and quality of life.
Difficulties in Problem-Solving and Abstract Thinking
At-risk individuals may face difficulties in problem-solving and abstract thinking. These cognitive skills are essential for logical reasoning, decision-making, and flexibility in thinking. Impairments in problem-solving and abstract thinking can limit an individual's ability to adapt to new situations, find effective solutions to challenges, and think creatively. These cognitive deficiencies can significantly impact an individual's overall cognitive functioning and inhibit their ability to perform daily tasks.
Connection Between Cognitive Stimulation and Brain Health
Neuroplasticity and Cognitive Stimulation
Cognitive stimulation plays a crucial role in maintaining and promoting brain health through the concept of neuroplasticity. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections and modifying existing ones in response to learning, experiences, and environmental influences. Engaging in cognitive stimulation exercises and activities can stimulate neuroplasticity, allowing the brain to adapt, change, and enhance its cognitive functions.
Effect of Cognitive Stimulation on Brain Function
The effect of cognitive stimulation on brain function is well-documented and supported by scientific research. Regular cognitive stimulation has been shown to improve neuronal connectivity, enhance synaptic plasticity, and increase the production of neurotrophic factors, all of which contribute to improved brain function. Moreover, cognitive stimulation can also lead to increased blood flow to the brain, promoting the delivery of oxygen and essential nutrients necessary for optimal brain health.

Potential Benefits of Cognitive Stimulation for At-Risk Individuals
Improvement in Memory and Thought Processes
Cognitive stimulation exercises have been found to improve memory and thought processes in at-risk individuals. By engaging in activities that challenge memory recall, such as word games or puzzles, individuals can strengthen their memory capacity and enhance their ability to retain and retrieve information. Furthermore, cognitive stimulation can also improve thought processes, allowing individuals to think more clearly, make connections, and engage in critical thinking.
Enhancement of Problem-Solving Abilities
Regular cognitive stimulation can enhance problem-solving abilities in at-risk individuals. Activities that involve complex problem-solving, such as Sudoku or logical reasoning puzzles, can improve an individual's cognitive flexibility, analytical thinking, and problem-solving strategies. By regularly engaging in such activities, at-risk individuals can sharpen their problem-solving skills, making them more adept at navigating daily challenges and finding effective solutions.
Reduction in Risk of Cognitive Decline
One of the most significant benefits of cognitive stimulation for at-risk individuals is the potential to reduce the risk of cognitive decline. Numerous studies have shown that consistent cognitive stimulation can effectively delay the onset of cognitive decline, including conditions such as mild cognitive impairment and dementia. By keeping the brain actively engaged and promoting neuroplasticity, cognitive stimulation can help maintain cognitive function and preserve brain health over time.
Current Evidence Supporting Cognitive Stimulation
Recent Research Findings
Recent research has provided compelling evidence supporting the effectiveness of cognitive stimulation for at-risk individuals. Multiple studies have demonstrated that cognitive stimulation exercises and interventions have the potential to improve cognitive performance and delay cognitive decline. These studies have shown positive outcomes in various cognitive domains, including memory, attention, executive functions, and language skills.
Case Studies of Cognitive Stimulation Effectiveness
Numerous case studies have highlighted the effectiveness of cognitive stimulation for at-risk individuals. These case studies often involve individuals at various stages of cognitive decline or impairment, including those with neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's. By implementing tailored cognitive stimulation programs, researchers and practitioners have observed significant improvements in cognitive function, quality of life, and overall well-being in these individuals.
Types of Cognitive Stimulation Exercises
Brain-Training Games and Puzzles
Brain-training games and puzzles are popular cognitive stimulation exercises that target various cognitive domains. These games often involve problem-solving, memory challenges, and attention exercises. Examples include Sudoku, crossword puzzles, memory matching games, and word association games. These activities not only provide mental stimulation but also offer entertainment and enjoyment for at-risk individuals.
Arts and Crafts, Music and Language Learning
Engaging in arts and crafts, music, and language learning can also offer cognitive stimulation for at-risk individuals. These activities require creativity, memory recall, attention, and executive functions. Painting, playing a musical instrument, learning new songs, or practicing a new language all provide opportunities for cognitive engagement and growth.
Physical Activities that Involve Cognitive Engagement
Physical activities that require cognitive engagement, such as dance classes, yoga, or tai chi, can provide a unique form of cognitive stimulation. These activities combine physical movement with mental focus and coordination, promoting brain activation while also benefiting overall physical health. Incorporating cognitive engagement into physical activities can lead to a holistic approach to cognitive stimulation for at-risk individuals.
Combining Cognitive Stimulation with Requisite Medical Treatment
Role of Medicines and Cognitive Therapy
While cognitive stimulation exercises play a crucial role in promoting brain health, they should not be seen as a standalone treatment for cognitive decline or impairment. Medical treatment, including prescription medicines and cognitive therapy, may be necessary depending on the individual's specific condition. Medications can help manage underlying medical conditions that contribute to cognitive decline, while cognitive therapy can provide targeted interventions to address cognitive deficiencies and enhance cognitive functioning.
Balancing Cognitive Stimulation with Treatment Plans
It is essential to strike a balance between cognitive stimulation and medical treatment plans. The integration of cognitive stimulation exercises and activities into an individual's treatment plan should be done collaboratively with healthcare professionals. By combining cognitive stimulation with requisite medical treatment, at-risk individuals can receive comprehensive care that addresses both the underlying causes of cognitive decline and promotes brain health.
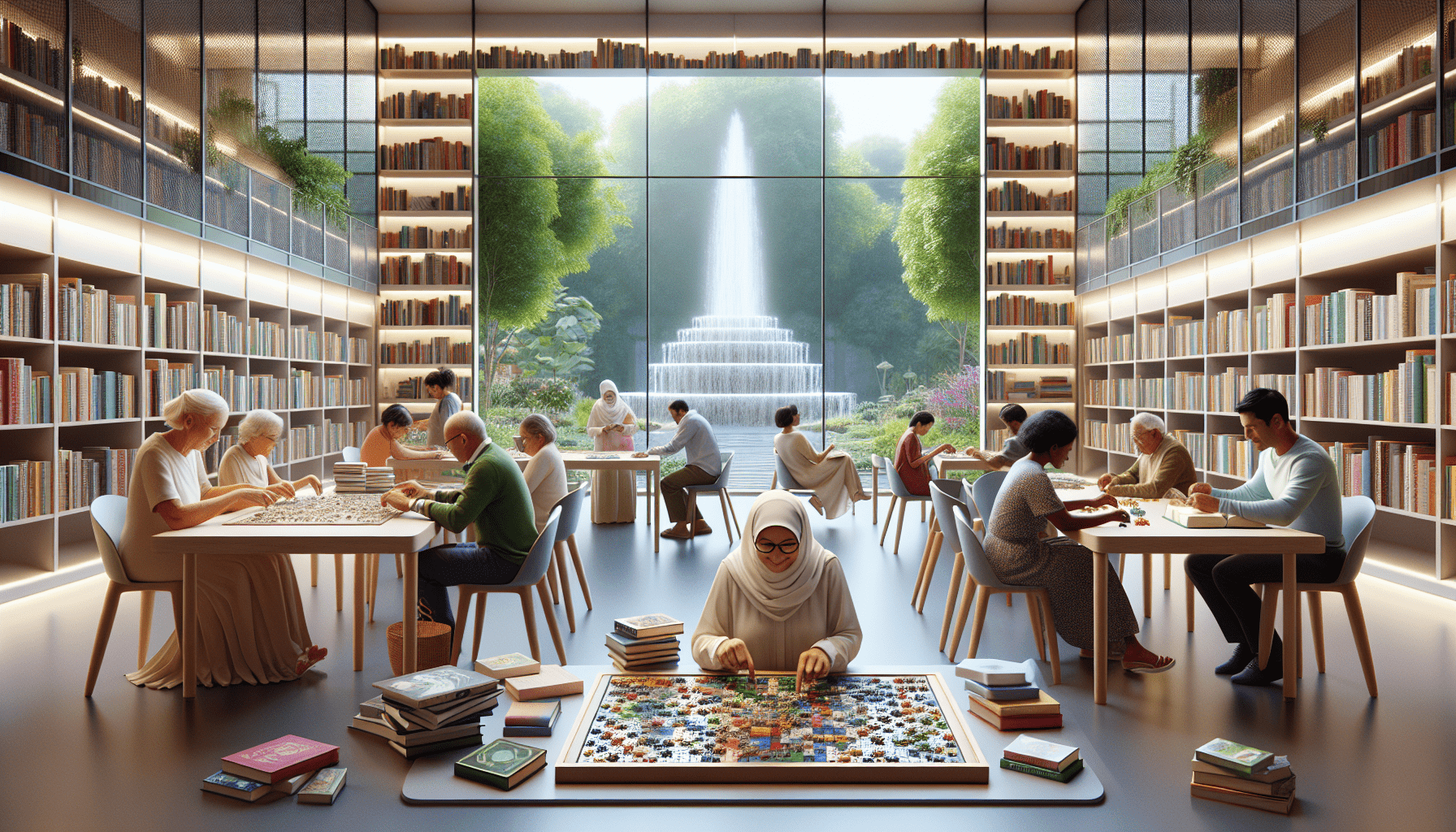

Challenges in Implementing Cognitive Stimulation Programs
Resistance from At-Risk Individuals
Implementing cognitive stimulation programs can sometimes face resistance from at-risk individuals. Some individuals may be skeptical about the effectiveness of cognitive stimulation exercises or reluctant to engage in new activities. Overcoming this resistance requires a patient-centered approach, open communication, and providing information about the potential benefits and scientific evidence supporting cognitive stimulation. Tailoring the activities to the individual's interests and preferences can also help increase motivation and engagement.
Ensuring Consistency and Progress Monitoring
Consistency and progress monitoring present challenges in cognitive stimulation programs. It is essential to establish consistent routines and schedules for cognitive stimulation activities, ensuring that at-risk individuals receive regular and ongoing cognitive engagement. Monitoring progress and evaluating the effectiveness of the interventions is crucial to make adjustments and optimize the cognitive stimulation program for each individual. Regular assessments and feedback can help track improvements and identify areas that require further attention.
Future Outlook for Cognitive Stimulation in At-Risk Populations
Latest Advancements and Their Potential
The field of cognitive stimulation continues to evolve, and new advancements are being made. The emergence of digital technologies has led to the development of innovative cognitive stimulation tools and apps that can be accessed on smartphones, tablets, or computers. Virtual reality technology is also being explored as a potential tool for cognitive stimulation. These advancements hold promising potential in enhancing the accessibility, personalization, and effectiveness of cognitive stimulation interventions.
Predicted Trends in Cognitive Stimulation Practices
Looking ahead, several trends in cognitive stimulation practices are predicted to emerge. Personalized cognitive stimulation programs that are tailored to individual needs and preferences are expected to become more prevalent. The integration of cognitive stimulation interventions into daily living environments, such as smart homes or community centers, can also enhance accessibility and long-term engagement. Moreover, the incorporation of cognitive stimulation into holistic wellness programs that integrate physical, mental, and social well-being is likely to become more common.
In conclusion, cognitive stimulation offers a promising approach for at-risk individuals to optimize brain health and maintain cognitive function. By engaging in cognitive stimulation exercises, at-risk individuals can improve their memory, problem-solving abilities, and overall cognitive performance. With a comprehensive understanding of cognitive stimulation, its benefits, and the challenges involved, healthcare professionals and individuals can work together to implement effective cognitive stimulation programs that promote brain health and well-being.